[ad_1]
For about a quarter century, Nvidia has been leading the revolution in computer graphics, becoming a beloved brand by gamers along the way.
Nvidia dominates the market for graphics processing units (GPUs), which it entered in 1999 with the GeForce 256. Gaming brought in over $9 billion in revenue for Nvidia last year despite a recent downturn.
But Nvidia’s latest earnings beat points to a new phenomenon in the GPU business. The technology is now at the center of the boom in artificial intelligence.
“We had the good wisdom to go put the whole company behind it,” CEO Jensen Huang told CNBC in an interview last month. “We saw early on, about a decade or so ago, that this way of doing software could change everything. And we changed the company from the bottom all the way to the top and sideways. Every chip that we made was focused on artificial intelligence.”
As the engine behind large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, Nvidia is finally reaping rewards for its early investment in AI. That’s helped to cushion the blow from broader semiconductor industry struggles tied to U.S.-China trade tensions and a global chip shortage.
Not that Nvidia is immune to geopolitical concerns. In October, the U.S. introduced sweeping new rules that banned exports of leading-edge AI chips to China. Nvidia counts on China for about one-quarter of its revenue, including sales of its popular AI chip, the A100.
“It was a turbulent month or so as the company went upside down to reengineer all of our products so that it’s compliant with the regulation and yet still be able to serve the commercial customers that we have in China,” Huang said. “We’re able to serve our customers in China with the regulated parts, and delightfully support them.”
AI will be a major focus of Nvidia’s annual GTC developer conference taking place from March 20-23. Ahead of the conference, CNBC sat down with Huang at Nvidia’s headquarters in Santa Clara, California, to discuss the company’s role at the heart of the explosion in generative AI.
“We just believed that someday something new would happen, and the rest of it requires some serendipity,” Huang said, when asked whether Nvidia’s fortunes are the result of luck or prescience. “It wasn’t foresight. The foresight was accelerated computing.”
GPUs are Nvidia’s primary business, accounting for more than 80% of revenue. Typically sold as cards that plug into a PC’s motherboard, they add computing power to central processing units (CPUs) built by companies like AMD and Intel.
Now, tech companies scrambling to compete with ChatGPT are publicly boasting about how many of Nvidia’s roughly $10,000 A100s they have. Microsoft said the supercomputer developed for OpenAI used 10,000 of them.
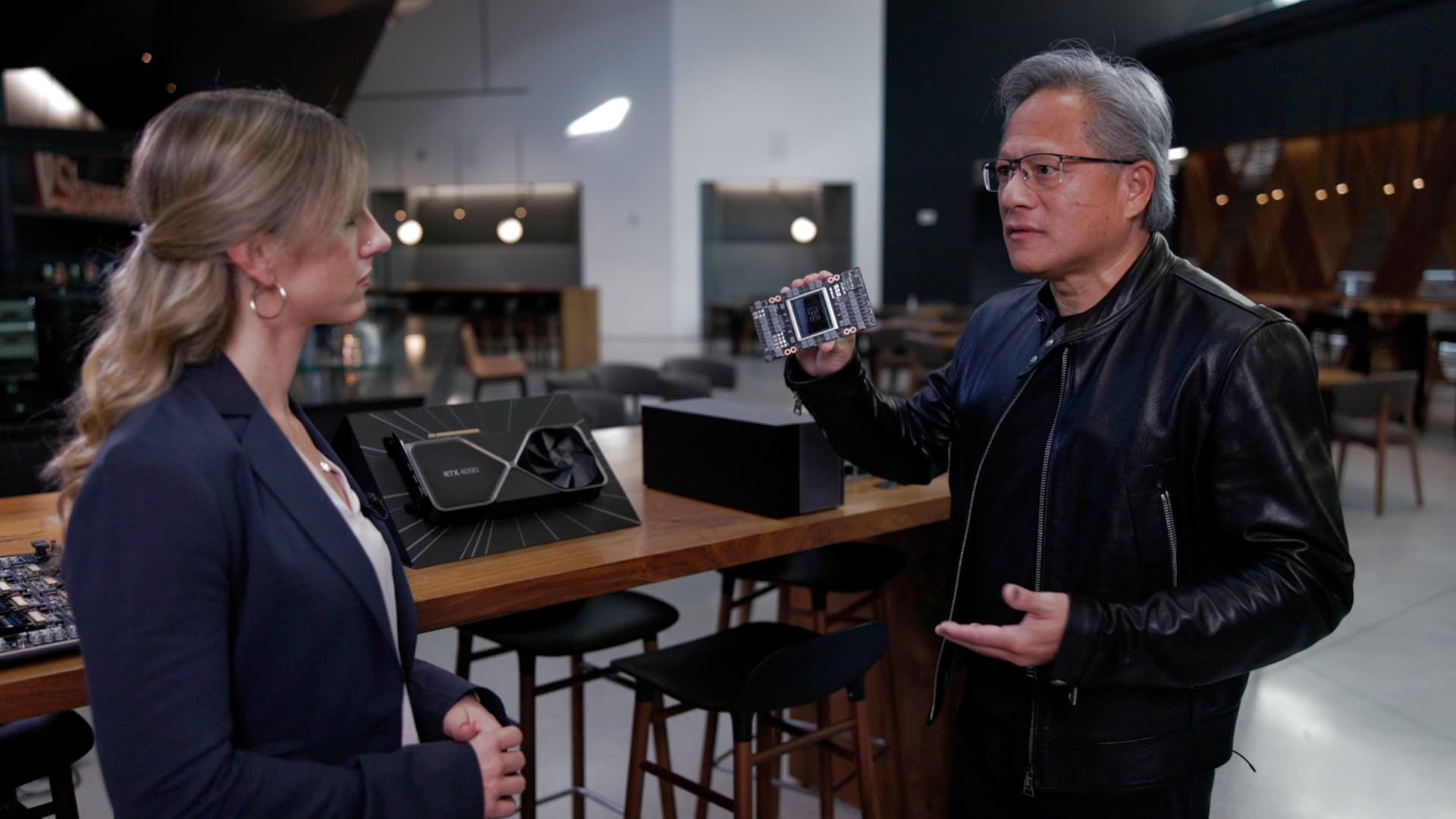
Nvidia Founder and CEO Jensen Huang shows CNBC’s Katie Tarasov a Hopper H100 SXM module in Santa Clara, CA, on February 9, 2023.
Andrew Evers
“It’s very easy to use their products and add more computing capacity,” said Vivek Arya, semiconductor analyst for Bank of America Securities. “Computing capacity is basically the currency of the valley right now.”
Huang showed us the company’s next-generation system called H100, which has already started to ship. The H stands for Hopper.
“What makes Hopper really amazing is this new type of processing called transformer engine,” Huang said, while holding a 50-pound server board. “The transformer engine is the T of GPT, generative pre-trained transformer. This is the world’s first computer designed to process transformers at enormous scale. So large language models are going to be much, much faster and much more cost effective.”
Huang said he “hand-delivered” to ChatGPT maker OpenAI “the world’s very first AI supercomputer.”
Not afraid to bet it all
Today, Nvidia is among the world’s 10 most valuable tech companies, with a market cap of close to $600 billion. It has 26,000 employees and a newly built polygon-themed headquarters. It’s also one of the few Silicon Valley giants with a founder of 30 years still at the helm.
Huang, 60, immigrated to the U.S. from Taiwan as a kid and studied engineering at Oregon State University and Stanford. In the early 1990s, Huang and fellow engineers Chris Malachowsky and Curtis Priem used to meet at a Denny’s and talk about dreams of enabling PCs with 3D graphics.
The trio launched Nvidia out of a condo in Fremont, California, in 1993. The name was inspired by NV for “next version” and Invidia, the Latin word for envy. They hoped to speed up computing so much that everyone would be green with envy — so they chose the envious green eye as the company logo.
Nvidia founders Curtis Priem, Jensen Huang and Chris Malachowsky pose at the company’s Santa Clara, California, headquarters in 2020.
Nvidia
“They were one among tens of GPU makers at that time,” Arya said. “They are the only ones, them and AMD actually, who really survived because Nvidia worked very well with the software community, with the developers.”
Huang’s ambitions and preference for impossible-seeming ventures have pushed the company to the brink of bankruptcy a handful of times.
“Every company makes mistakes and I make a lot of them,” said Huang, who was one of Time magazine’s most influential people in 2021. “Some of them put the company in peril, especially in the beginning, because we were small and we’re up against very, very large companies and we’re trying to invent this brand-new technology.”
In the early 2010s, for example, Nvidia made an unsuccessful move into smartphones with its Tegra line of processors. The company then exited the space.
In 1999, after laying off the majority of its workforce, Nvidia released what it claims was the world’s first official GPU, the GeForce 256. It was the first programmable graphics card that allowed custom shading and lighting effects. By 2000, Nvidia was the exclusive graphics provider for Microsoft’s first Xbox. In 2006, the company made another huge bet, releasing a software toolkit called CUDA.
“For 10 years, Wall Street asked Nvidia, ‘Why are you making this investment? No one’s using it.’ And they valued it at $0 in our market cap,” said Bryan Catanzaro, vice president of applied deep learning research at Nvidia. He was one of the only employees working on AI when he joined Nvidia in 2008. Now, the company has thousands of staffers working in the space.
“It wasn’t until around 2016, 10 years after CUDA came out, that all of a sudden people understood this is a dramatically different way of writing computer programs,” Catanzaro said. “It has transformational speedups that then yield breakthrough results in artificial intelligence.”
Although AI is growing rapidly, gaming remains Nvidia’s primary business. In 2018, the company used its AI expertise to make its next big leap in graphics. The company introduced GeForce RTX based on what it had learned in AI.
“In order for us to take computer graphics and video games to the next level, we had to reinvent and disrupt ourselves, change literally what we invented altogether,” Huang said. “We invented this new way of doing computer graphics, ray tracing, basically simulating the pathways of light and simulate everything with generative AI. And so we compute one pixel and we imagine with AI the other seven.”
‘Boom-or-bust cycle’
From the beginning, Huang was committed to making Nvidia a fabless chip company, or one that designs the product but contracts out production to others that have chip fabrication plants, or fabs. Nvidia keeps capital expenditure down by outsourcing the extraordinary expense of making the chips to Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company.
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company’s U.S. office space in San Jose, CA, in 2021.
Katie Tarasov
Investors are right to be concerned about that level of dependence on a Taiwanese company. The U.S. passed the CHIPS Act last summer, which sets aside $52 billion to incentivize chip companies to manufacture on U.S. soil.
“The biggest risk is really U.S.-China relations and the potential impact of TSMC. If I’m a shareholder in Nvidia, that’s really the only thing that keeps me up at night,” said C.J. Muse, an analyst at Evercore. “This is not just a Nvidia risk, this is a risk for AMD, for Qualcomm, even for Intel.”
TSMC has said it’s spending $40 billion to build two new chip fabrication plants in Arizona. Huang told CNBC that Nvidia will “absolutely” use TSMC’s Arizona fabs to make its chips.
Then there are questions about demand and how many of the new use cases for GPUs will continue to show growth. Nvidia saw a spike in demand when crypto mining took off because GPUs became core to effectively competing in that market. The company even created a simplified GPU just for crypto. But with the cratering of crypto, Nvidia experienced an imbalance in supply and demand.
“That has created problems because crypto mining has been a boom-or-bust cycle,” Arya said. “Gaming cards go out of stock, prices get bid up, and then when the crypto mining boom collapses, then there is a big crash on the gaming side.”
Nvidia caused major sticker shock among some gamers last year by pricing its new 40-series GPUs far higher than the previous generation. Now there’s too much supply and, in the most recent quarter, gaming revenue was down 46% from a year earlier.
Competition is also increasing as more tech giants design their own custom-purpose chips. Tesla and Apple are doing it. So are Amazon and Google.
“The biggest question for them is how do they stay ahead?” Arya said. “Their customers can be their competitors also. Microsoft can try and design these things internally. Amazon and Google are already designing these things internally.”
For his part, Huang says that such competition is good.
“The amount of power that the world needs in the data center will grow,” Huang said. “That’s a real issue for the world. The first thing that we should do is: every data center in the world, however you decide to do it, for the goodness of sustainable computing, accelerate everything you can.”
In the car market, Nvidia is making autonomous-driving technology for Mercedes-Benz and others. Its systems are also used to power robots in Amazon warehouses, and to run simulations to optimize the flow of millions of packages each day.
Huang describes it as the “omniverse.”
“We have 700-plus customers who are trying it now, from [the] car industry to logistics warehouses to wind turbine plants,” Huang said. “It represents probably the single greatest container of all of Nvidia’s technology: computer graphics, artificial intelligence, robotics and physics simulation, all into one. And I have great hopes for it.”
[ad_2]